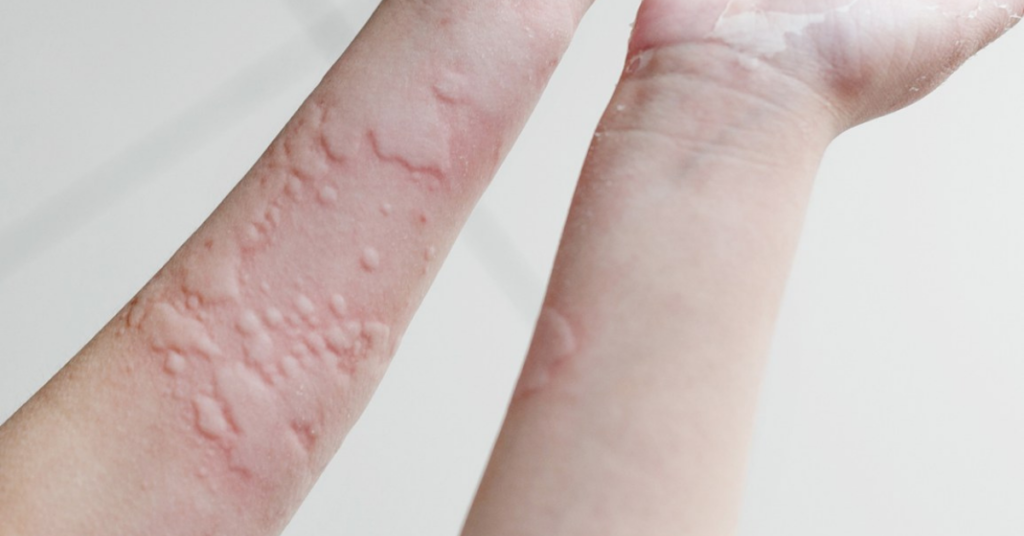
Urticaria,also known as Hives is a disease which is characterized by the sudden development of itchy and swollen bumps on the skin. These bumps can appear if the body reacts to any allergens or can even appear for reasons not known. They last for less than 1-2 days in the same spot and once they disappear, they don’t leave any trace/scar behind. However, when these bumps develop under the skin, the condition is termed as Angioedema.
Urticaria is classified into Acute and Chronic urticaria depending upon the time period it lasts for.
- Acute Urticaria- When urticaria lasts for less than 6 weeks, it is termed as acute urticaria.
Causes:
- Allergic ( food, medications, insect bite)
- Infectious ( Viral, bacterial or parasitic)
- Idiopathic ( No cause identified: Many cases are likely to be because of a viral in an organ)
2. Chronic Urticaria- When urticaria lasts for more than 6 weeks, it is termed as chronic urticaria.
Causes:
- Spontaneous (90%)
- Autoimmune or idiopathic
- Inducible (10%)
Physical
- Demographic- From heat/cold
- Aquagenic- Due to water
- Cholinergic- Due to physical exertion/ Temperature changes
- Pressure
Treatment of Urticaria
- Acute Urticaria- The primary way of treating acute urticarial is to avoid the trigger if possible.
- In case of severe angioedema involving throat which in turn causes difficulty in breathing, epinephrine is used.
- Otherwise, anti-allergic medicines like hydroxyzine, cetirizine, levocetirizine and fexofenadine are used.
- Chronic Urticaria- Majority of the patients are controlled with anti-allergic medicines. Sometimes, the addition of montelukast may help. Other immunomodulator medicines and biological agents can be used in refractory cases